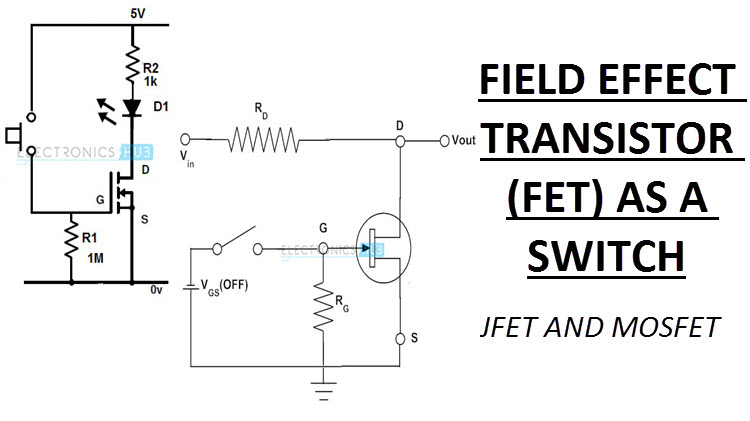
FET (Field-Effect Transistor) Basics Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) are unipolar devices, and have two big advantages over bipolar transistors: one is that they have a near-infinite input resistance and thus offer near-infinite current and power gain; the other is that their switching action is not marred by charge-storage problems, and they thus outperform most bipolars in terms of digital switching speeds.

- Information regarding the use of FCNs was made public by an announcement in the Federal Register on April 12, 2010. Publication 3536 - Motor Fuel Excise Tax EDI Guide This publication is designed to provide the general requirements, specifications and procedures for the electronic filing of Internal Revenue Service (IRS) Form 720-TO, Terminal.
- When cascaded, we can connect more such gates to the source FET since the current drawn is negligible, not loading the source FET. We call this as an “increased Fan-out” Current drawn and hence power dissipated is less, making it ideal for hand held battery operated devices and other instruments like laptops, mobile phones, tablets etc.
- A succession of FET-like devices was patented by Julius Lilienfeld in the 1920s and 1930s. However, materials science and fabrication technology would require decades of advances before FETs could actually be manufactured. JFET was first patented by Heinrich Welker in 1945. During the 1940s, researchers John Bardeen, Walter Houser Brattain, and William Shockley were trying to build a.
FET Applications:
Use Of Fetus In Vaccines
What are the various applications of the Field Effect Transistor?
In this short post let us discuss about the various applications of FET - Field Effect Transistor. Before proceeding further it is good to refresh about the basics of FET.
The Field Effect Transistor (FET) is a semiconductor device which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. Thus it is called as FET.

There are two types FET
- Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET) or simply FET.
- Insulated Gate Field Effect Transistor IGFET.
It is also called as Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) transistor or MOSFET.
Applications of Field Effect Transistor (FET):
Use Of Fetal Cell Lines
- FET has high input impedance and low output impedance. So it is used as a buffer in measuring instruments, receivers.
- FET has low noise operation. So it is used in RF amplifiers in FM tuners and communication equipment.
- FET has low input capacitance, so it is used in cascade amplifiers in measuring and test equipment.
- Since FET is a voltage controlled device, it is used as a voltage variable resistor in operational amplifiers and tone controls.
- FET has low inner modulation distortion. So it is used in mixer circuits in FM and TV receivers, and communication equipment.
- Since it is low-frequency drifts, it is used in oscillator circuits.
- FETs are used in low-frequency amplifiers in hearing aids and inductive transducers, as the coupling capacitor is small.
- Since FET occupying less space and easy to fabricate, it is used in digital circuits in computers, LSD and memory circuits.
Thanks for reading about Applications of FET... Please leave your comments below... Please subscribe to get more posts to your mail ID...
You May also like to Read:
Crystal oscillator - Basics, Working, Frequency Response, Pros & Cons
Comparison between Synchronous Motor and 3-Phase Induction Motor
Electrical Braking System Advantages Limitations Disadvantages
Simple Arduino Project - Serial Communication Demonstration Project