ATOMIC NUMBER 5 Dictionary entry overview: What does atomic number 5 mean?. ATOMIC NUMBER 5 (noun) The noun ATOMIC NUMBER 5 has 1 sense. A trivalent metalloid element; occurs both in a hard black crystal and in the form of a yellow or brown powder Familiarity information: ATOMIC NUMBER 5 used as a noun is very rare. Answers for Atomic number 5 crossword clue. Search for crossword clues found in the Daily Celebrity, NY Times, Daily Mirror, Telegraph and major publications. Find clues for Atomic number 5 or most any crossword answer or clues for crossword answers. What is the atomic symbol for silver? What is the atomic mass of mercury? Ni is the symbol for what element? The element that has the atomic number 17 is? List the symbols for two transition metals. Cu, Ag, and Au are all in what group # 11 7. Name two noble gases Any in Group 18 8.
The periodic table is an arrangment of the chemical elements ordered by atomic number so that periodic properties of the elements (chemical periodicity) are made clear.
Each element is identified by the number of protons in its atoms. This number is the atomic number. The periodic table lists the elements in order of increasing atomic number. Each element has a symbol, which is one or two letters. The first letter is always capitalized. If there is a second letter, it is lowercase. Atomic number 5 (2, 3) 7 (2, 5) 10(2, 8) (i) Element A belongs to group 13 (Group No. It is boron (B) (ii) Element B belongs to group 15 (Group No. It is nitrogen (N) Both these elements belong to second period since they have two shells. Write two reasons responsible for the late discovery of noble.
Explore the chemical elements through this periodic table


| Group | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Period 1 | Hydrogen | Helium | |||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Lithium | Beryllium | Boron | Carbon | Nitrogen | Oxygen | Fluorine | Neon | |||||||||||
| 3 | Sodium | Magnesium | Aluminium | Silicon | Phosphorus | Sulfur | Chlorine | Argon | |||||||||||
| 4 | Potassium | Calcium | Scandium | Titanium | Vanadium | Chromium | Manganese | Iron | Cobalt | Nickel | Copper | Zinc | Gallium | Germanium | Arsenic | Selenium | Bromine | Krypton | |
| 5 | Rubidium | Strontium | Yttrium | Zirconium | Niobium | Molybdenum | Tc☢ Technetium | Ruthenium | Rhodium | Palladium | Silver | Cadmium | Indium | Tin | Antimony | Tellurium | Iodine | Xenon | |
| 6 | Caesium | Barium | * | Lutetium | Hafnium | Tantalum | Tungsten | Rhenium | Osmium | Iridium | Platinum | Gold | Mercury | Thallium | Lead | Bismuth | Po☢ Polonium | At☢ Astatine | Rn☢ Radon |
| 7 | Fr☢ Francium | Ra☢ Radium | ** | Lr☢ Lawrencium | Rf☢ Rutherfordium | Db☢ Dubnium | Sg☢ Seaborgium | Bh☢ Bohrium | Hs☢ Hassium | Mt☢ Meitnerium | Ds☢ Darmstadtium | Rg☢ Roentgenium | Cn☢ Copernicium | Nh☢ Nihonium | Fl☢ Flerovium | Mc☢ Moscovium | Lv☢ Livermorium | Ts☢ Tennessine | Og☢ Oganesson |
| *Lanthanoids | * | Lanthanum | Cerium | Praseodymium | Neodymium | Pm☢ Promethium | Samarium | Europium | Gadolinium | Terbium | Dysprosium | Holmium | Erbium | Thulium | Ytterbium | ||||
| **Actinoids | ** | Ac☢ Actinium | Th☢ Thorium | Pa☢ Protactinium | U☢ Uranium | Np☢ Neptunium | Pu☢ Plutonium | Am☢ Americium | Cm☢ Curium | Bk☢ Berkelium | Cf☢ Californium | Es☢ Einsteinium | Fm☢ Fermium | Md☢ Mendelevium | No☢ Nobelium | ||||
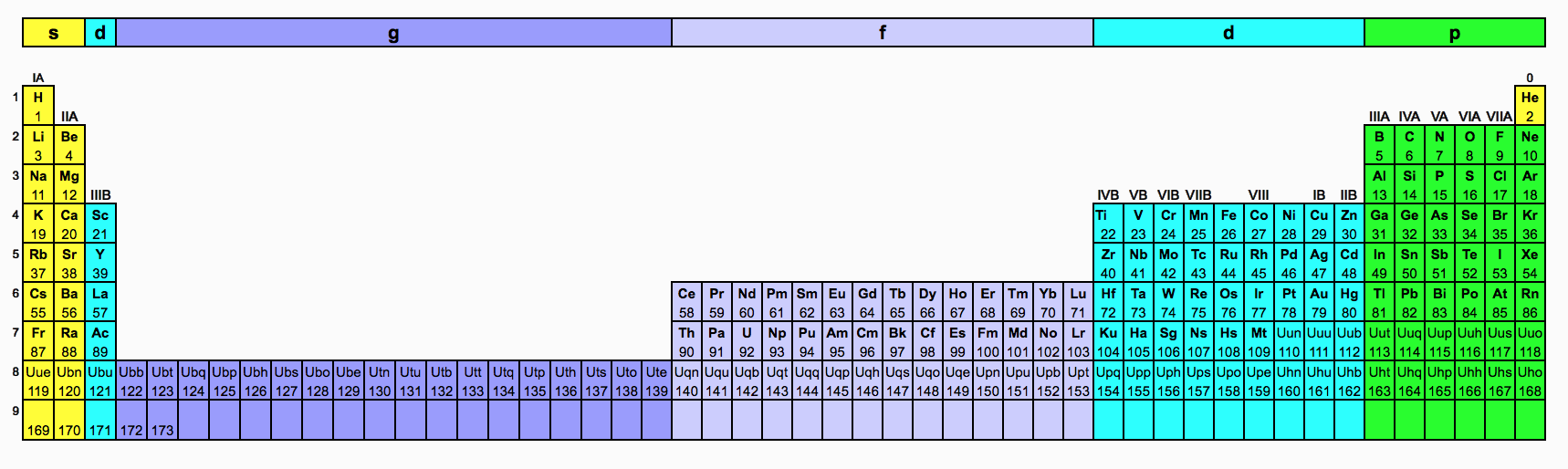
The standard form of the periodic table shown here includes periods (shown horizontally) and groups (shown vertically). The properties of elements in groups are similar in some respects to each other.
Atomic Number Chart

Atomic Number 57
There is no one single or best structure for the periodic table but by whatever consensus there is, the form used here is very useful and the most common. The periodic table is a masterpiece of organised chemical information and the evolution of chemistry's periodic table into the current form is an astonishing achievement.
